NephroPath platform
Through the NephroPath platform, we provide a detailed evaluation of histological biomarkers in preclinical and clinical kidney samples1. Our AI-based quantification offers reproducible, consistent, fast, and more detailed scoring of renal pathology biomarkers compared to traditional human reading.
Explore our image analysis services and partner with us to improve your (pre)clinical studies.
1. The NephroPath platform is for Research Use Only and should not be used for diagnostic procedures.
AI-assisted image analysis services
-
Standard whole kidney analysis
-
Custom kidney analysis
-
Enrich your study with AI-powered whole kidney tissue quantification. We offer insights into your data through:
Accurate segmentation and delineation of relevant kidney structures
Extent of glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis
(Immune) cell quantification, including spatial relation to tissue
Online/offline access to all results
-
Leverage Aiosyn’s expertise in AI and the latest technology to create a tailored analysis for kidney tissue. We offer development and prototyping of robust and performant models with a quick turn-around time:
IHC/Biomarker quantification in specific animal models
Treatment response grouping
Tissue microenvironment analysis
How can we assist your team?
- Detailed reports on kidney tissue analysis swiftly upon data submission.
- Precise quantification to improve the reproducibility of results.
- Improved objectivity of pathologist’s assessments in multi-center (pre)clinical studies.
- Customized projects for new and existing biomarkers.
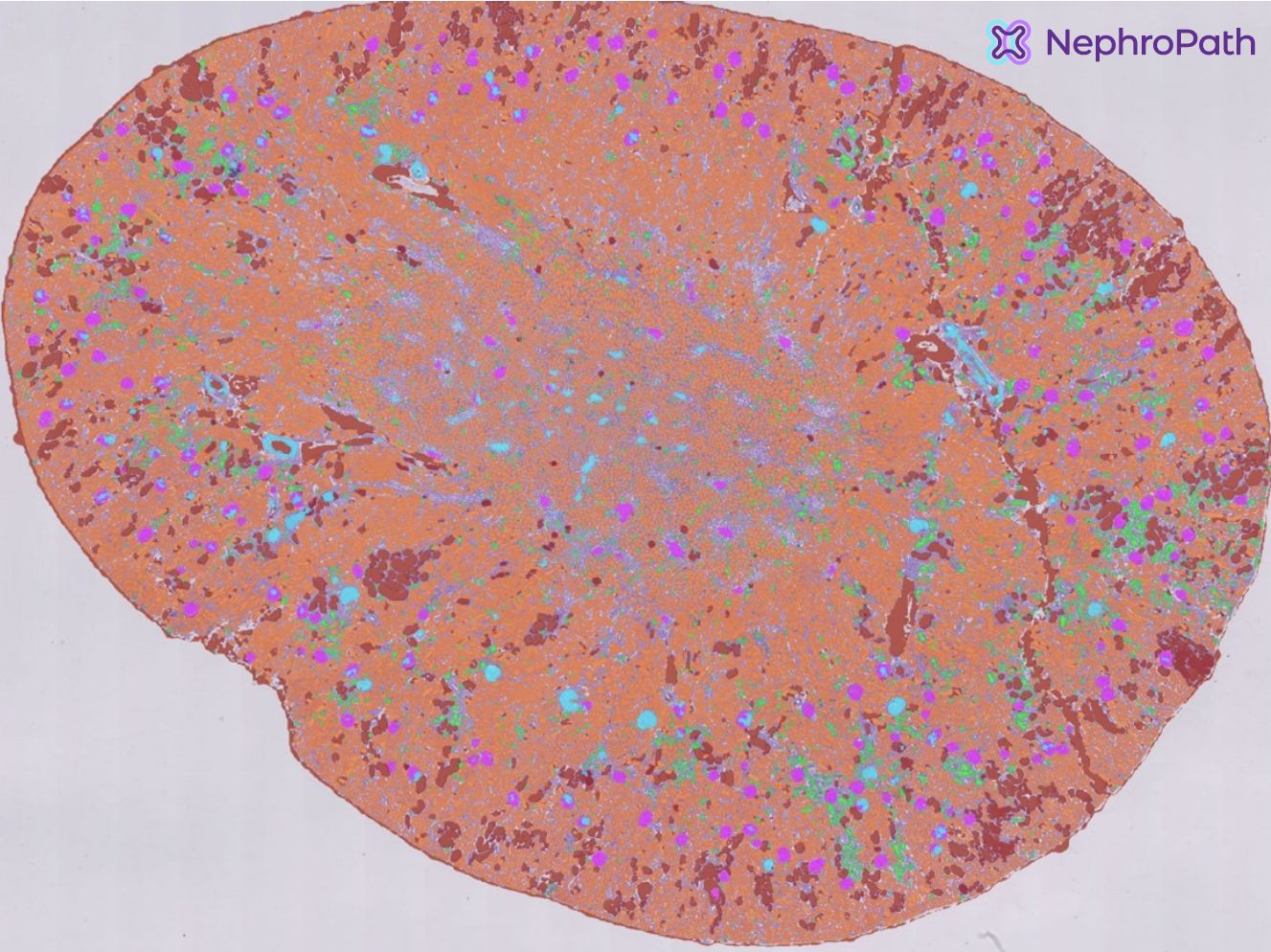
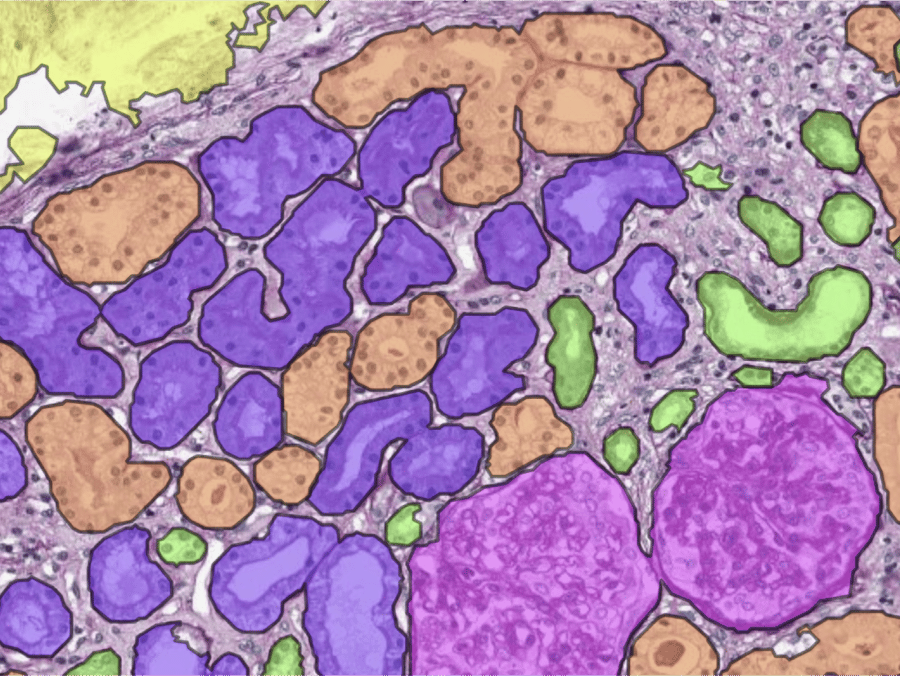
Segmentation of main tissue classes
Our AI can accurately segment relevant kidney structures, among which: (sclerotic) glomeruli, proximal/distal/atrophic tubuli, arteries & capsule. Leveraging this data, we can provide a wide variety of quantitative and spatial measurements, such as the number of glomeruli in a biopsy or the tissue area consisting of interstitium.
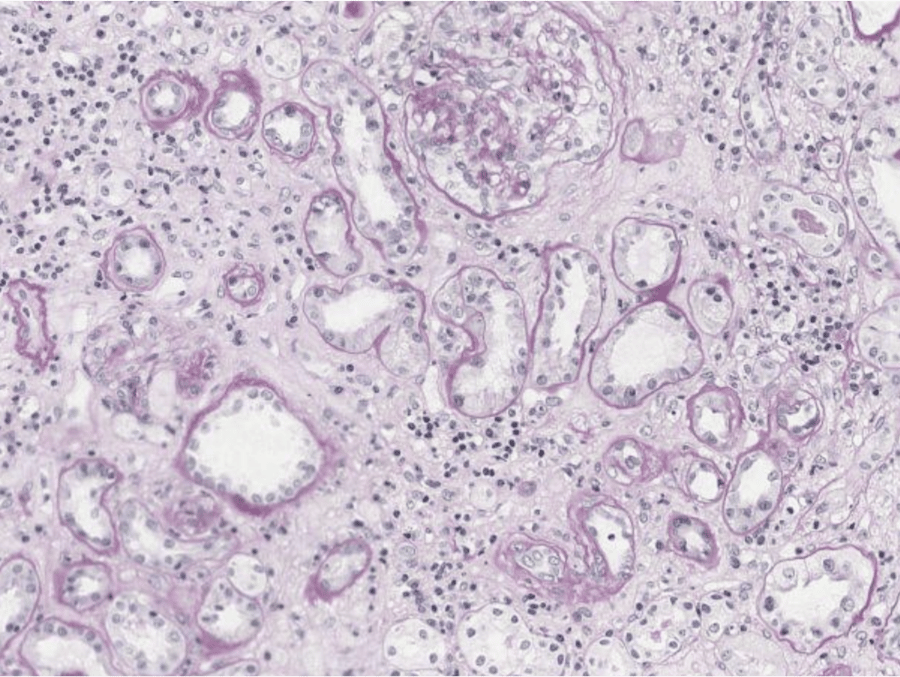

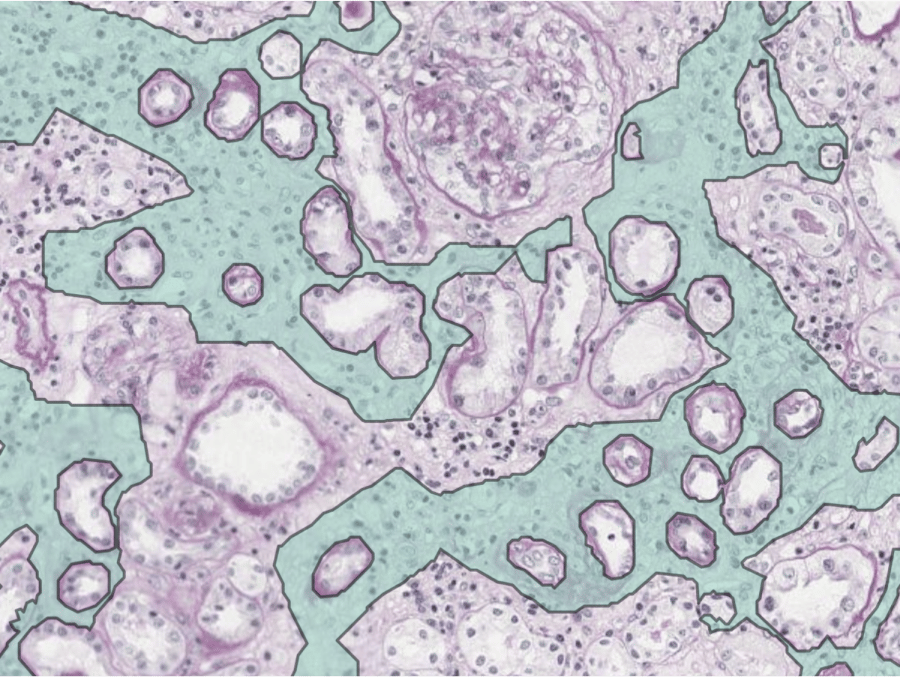
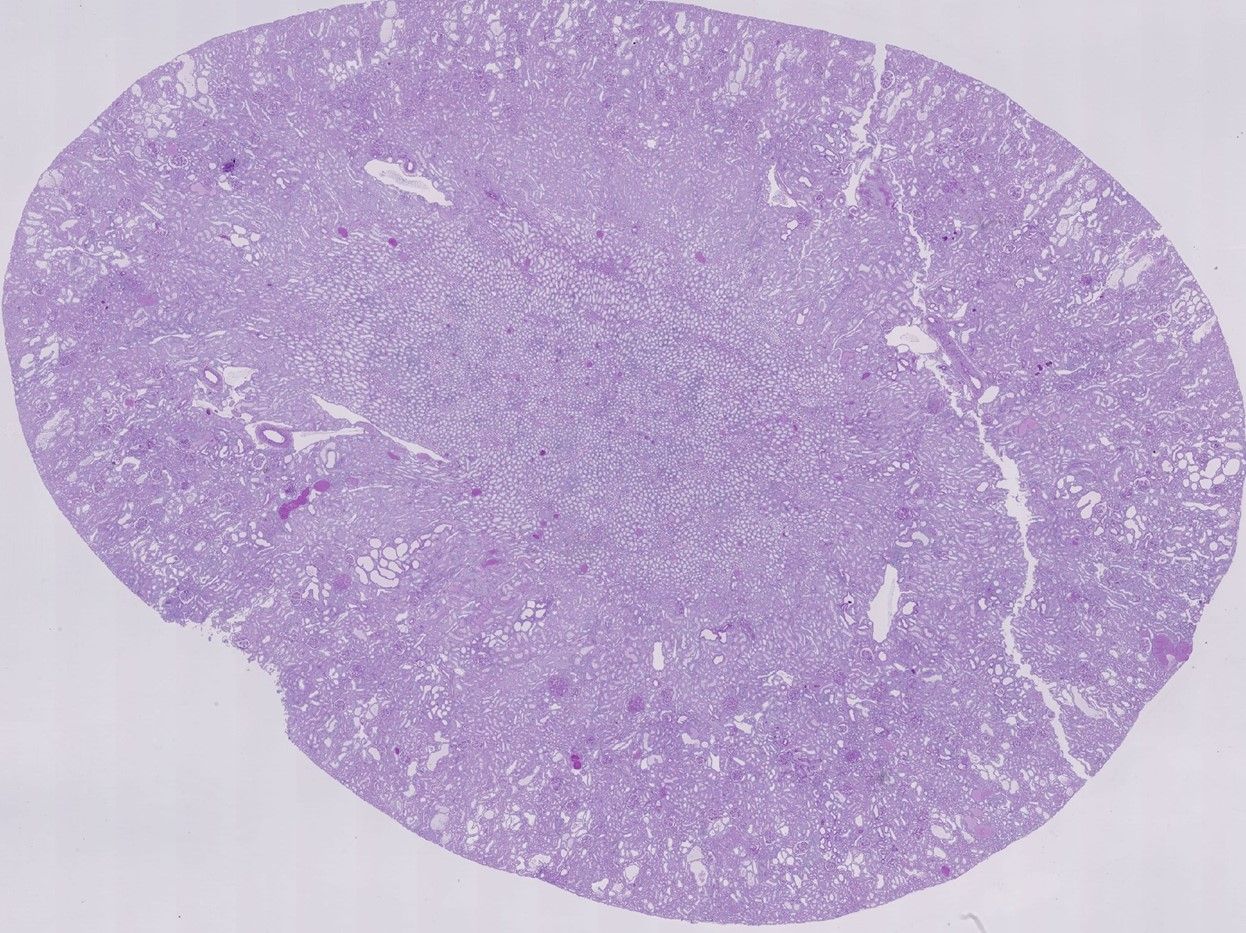
AI-Powered quantification of fibrosis
Renal fibrosis is a key biomarker for CKD progression and for prognosis of kidney transplantation. Current scoring systems are based on crude semi-quantitative assessments, limited to the capability of the human eye. AI-based fibrosis quantification yields an objective and precise measurement that can aid pathologists and biopharma services with their assessments.
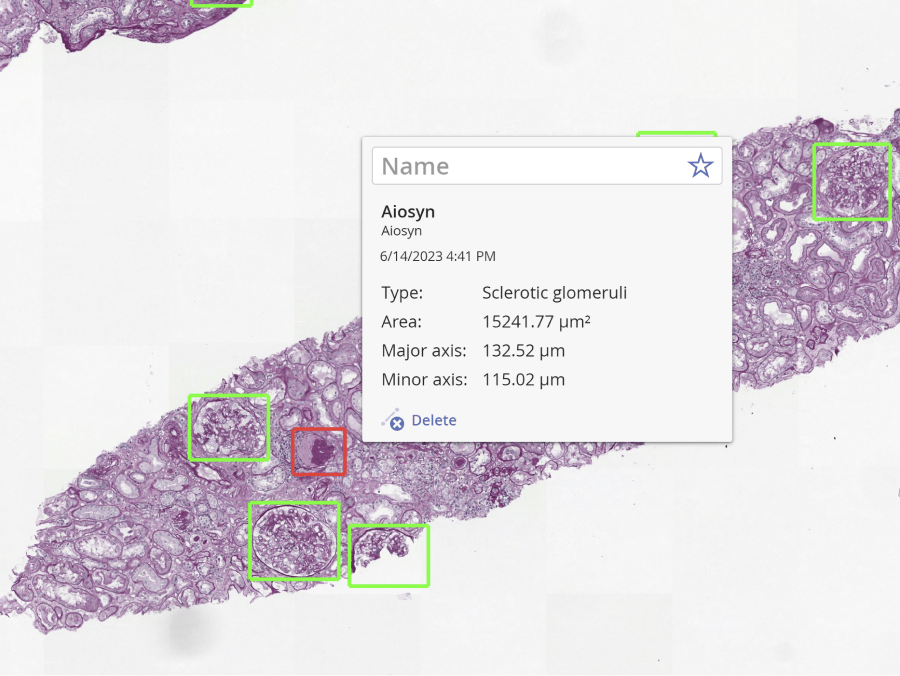
Localization and counting of glomeruli
The assessment of glomeruli is a quality assessment of every renal sample. Our AI-powered algorithms provide a quantitative glomerular count, boosting the efficiency and reproducibility of kidney tissue evaluations.
NephroPath platform news
-
Aiosyn and HistoWiz partner to improve kidney disease research through AI-powered preclinical studies
22 May, 2024 • By Anna Correas GrifollRead more -
Aiosyn and Physiogenex partner to enhance kidney disease drug development
14 March, 2024 • By Kama WitkowskaRead more -
Aiosyn announces the formation of a Scientific Advisory Board to guide the continued development of its Kidney AI Suite
12 October, 2023 • By Anna Correas GrifollRead more
Questions? We are happy to answer
We will get back to you as soon as possible.








